Join our Mailing list!
Join us as we embark on a journey of making it practical for people to spend their Bitcoin anywhere they want to.
No matter who you talk to about Bitcoin, the first thing that will probably be talked about is its price.
Very few who hold Bitcoin go about their day without checking price of Bitcoin at least once.
It’s the most searched term on search engines, no matter the geographical area. It has given rise to memes, heroes and villains in the industry. It determines whether certain companies survive or go bankrupt. It impacts how much attention the industry as a whole gets from the general public.
Therefore, it is safe to say that understanding the mechanics behind Bitcoin’s price and action and learning some jargon will prove quite useful in the journey of understanding Bitcoin.
The Bitcoin market is a global financial ecosystem centered around the buying and selling of Bitcoin. Open 24/7/365, it consists of various platforms where individuals can buy, sell, and trade Bitcoin.
There are various types of markets where market participants buy, sell and speculate using Bitcoin. These can be divided into 4 basic categories:
The Bitcoin spot market refers to the market for buying and selling actual Bitcoin. It is where Bitcoin is bought and sold for immediate delivery and settlement. Transactions in the spot market involve the actual exchange of Bitcoin between the buyer and the seller. Spot markets act as the reference point for the market price of Bitcoin. They operate on an ‘orderbook’ system where the orders of buyers and sellers are matched to enable to the exchange of Bitcoin between market participants.
In a P2P Bitcoin market, buyers and sellers transact directly with each other without the involvement of intermediaries like exchanges. P2P platforms connect buyers with sellers, allowing them to negotiate terms and execute trades.
The derivatives market involves financial instruments whose value is derived from the price action of Bitcoin. Bitcoin derivatives include futures and options contracts, allowing traders to speculate on the future price of Bitcoin without owning any. Derivatives can be traded on specialised Bitcoin derivatives exchanges, providing additional tools for risk management and speculation.
The OTC market involves direct trades between buyers and sellers, often facilitated by brokers or market makers.
OTC trades are typically conducted off-exchange, providing privacy and catering to larger institutional investors, high-net-worth individuals or Bitcoin miners. OTC desks facilitate large Bitcoin trades with negotiated terms, catering to participants who may require liquidity beyond what is available on spot exchanges.
Since the ecosystem uses the spot market as a reference point to obtain the current market price of Bitcoin, let’s take a closer look at how price moves on these platforms.
Bitcoin exchanges operate on an order book system, which is essentially a real-time ledger of buy and sell orders placed by traders. Bids, representing buy orders, and asks, representing sell orders, populate this order book with corresponding prices and quantities.
The highest bid and the lowest ask form the “top of the book.”
The bid-ask spread is a critical component of the order book. Bids reflect the prices at which buyers are willing to purchase Bitcoin, while asks represent the prices at which sellers are willing to sell. The bid-ask spread is the difference between the highest bid and the lowest ask. A narrower spread generally indicates higher liquidity, making it easier for traders to execute transactions without significant price impact.
Here is what a typical exchange orderbook looks like
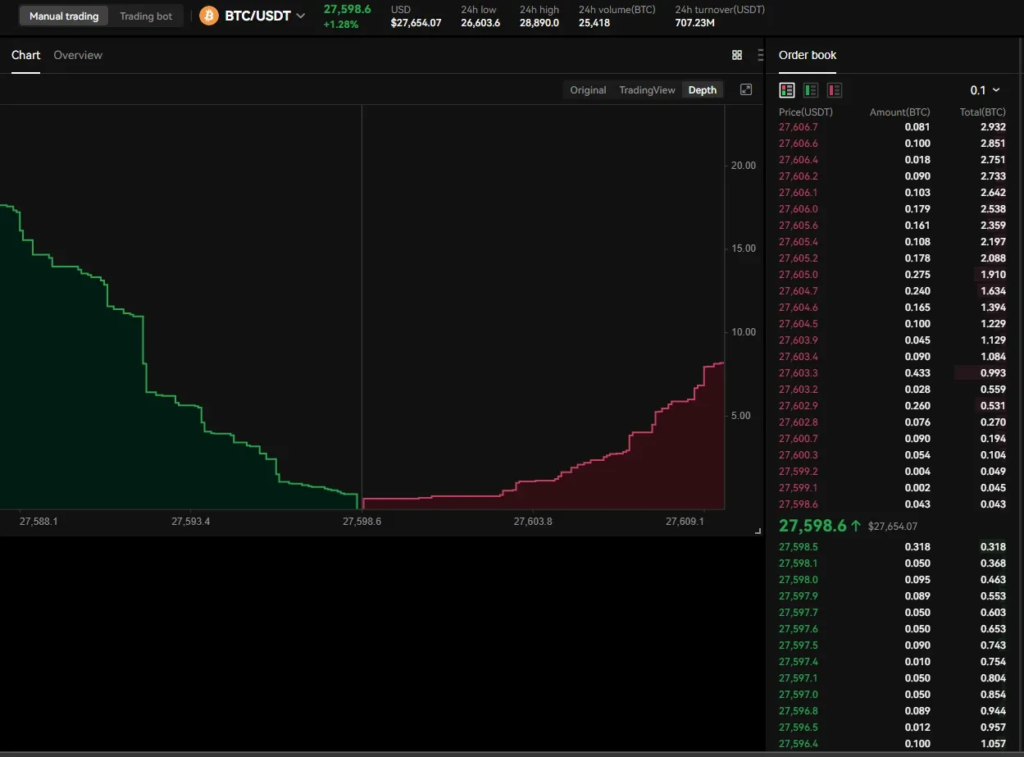
Image source: OKX
Every trader can make two types of orders on an exchange, be it a bid or an ask order:
Market Order: Executed immediately at the current market price. Happens instantly.
Limit Order: Set at specific prices and remain in the order book until a matching market order is found. Happens depending on existing orders in the orderbooks.
The use of these order types reflects trader preferences and strategies in navigating the market.
In the Bitcoin ecosystem, ‘Whales’ are entities that frequently post large bid or ask orders on an exchange. Their orders can usually be identified by looking at an orderbook.
The size of orders, particularly large buy or sell orders, can significantly influence the Bitcoin market. A substantial market buy order, for instance, may absorb available sell orders up to a certain price, leading to a price increase. Conversely, a sizable market sell order can deplete available buy orders and contribute to a decrease in price.
A liquid market is characterised by a high number of participants and a tight bid-ask spread, allowing for smoother buying and selling. Higher liquidity generally leads to more stable prices, while lower liquidity can result in price slippage, where the execution price deviates from the expected price.
Combining these two factors, large orders in a highly illiquid market condition can lead to huge swings in price, leading to a widespread belief that prices are being constantly manipulated.
Liquidity providers are entities or participants who contribute to the overall liquidity by offering to buy or sell Bitcoin. Their goal is to facilitate faster matching of orders and ensure that there are enough buyers and sellers in the market to execute transactions smoothly.
They do this by placing a variety of buy and sell orders at different price levels. This makes it easier for traders to execute transactions without causing significant price fluctuation.This reduces the impact of large trades on Bitcoin prices and contributes to creating a more stable and orderly market.
Liquidity providers can be individual traders, institutional investors, trading firms or even exchanges themselves.
Market makers are a type of liquidity providers who actively quote both buy (bid) and sell (ask) orders in the market. Their primary goal would be to profit from the bid-ask spread that we talked about earlier, which is the difference between the highest price a buyer is willing to pay and the lowest price a seller is willing to accept.
They continuously quote bid and ask prices, indicating their willingness to buy or sell at those levels. This activity contributes to the liquidity of the market. The primary motivation is to seek to profit from the spread by capturing the price difference between their buy and sell quotes. They aim to do this repeatedly as they facilitate trades.
Through their continuous presence and active quoting, market makers help mitigate price volatility by providing stability to the order book. Because of this, they play a crucial role in maintaining a stable order book. Their strategies contribute to preventing sudden imbalances in buying or selling pressure that could lead to extreme price swings.
Higher participation and a broader range of market participants could increase liquidity. This could lead to orderbooks being more populated and hence a higher likelihood of orders being matched. Market price won’t fluctuate as much as a result.
Exchanges can implement market-making programs on your exchange to add liquidity. This involves incentivizing traders to place both buy and sell orders, narrowing the bid-ask spread and making it easier for users to execute trades without causing significant price movements.
Exchanges can attract liquidity providers by offering rewards or reduced fees for those who commit to maintaining a certain level of liquidity. This can help stabilise the orderbook and reduce the impact of large market orders.
In addition to market-making programs, liquidity provider programs can be implemented by exchanges to attract entities or participants who contribute to overall liquidity. These programs offer rewards or reduced fees to those who commit to maintaining a certain level of liquidity. By doing so, the order book can be stabilized, and the impact of large market orders can be reduced.
Overall, these measures aim to create a more stable and orderly market environment, reducing the potential for extreme price swings.
Overall, price of Bitcoin is purely driven by the dynamics of supply and demand. Its value is solely determined by the open, global market by various participants making economic interactions with each other.
Hope this article has helped you get an insight into the mechanics of Bitcoin’s price action.
If you are looking for the most reliable solution to easily liquidate, sell Bitcoin to instantly receive Euros into bank account, get access to you Bringin IBAN account today.

Contact us at [email protected]
© 2023 UAB Bringin. All right reserved
Vilnius, J. Savickio st. 4-7,
Lithuania – LT-01108
Join us as we embark on a journey of making it practical for people to spend their Bitcoin anywhere they want to.